This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We\'ll assume you\'re ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Read More
Measuring the how and why in conversational data with artificial intelligence and deep learning
Two truths are widely understood. The first is that technology is becoming more ubiquitous in our society as algorithmic capabilities expand and increasingly inventive ideas are brought forth. The second is that businesses, now more than ever, require extreme efficiency, improved quality, and reduced costs. In order to gain competitive advantages, executives must stay atop the latest trends in technological offerings.
By tracking the flow of an interaction, BSP algorithms can determine what behaviors and emotions caused a reaction and when there were turning points. These insights can then be transformed into analytic reports and eventually teaching tools, deriving true value from often-disregarded unstructured data.
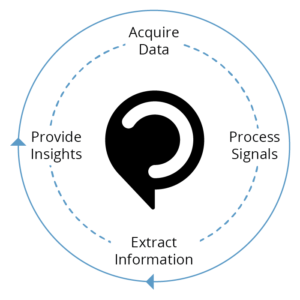
Fig.1a Behavioral Signals Data-to-Insights lifecycle.
Behavioral Signal Technologies, Inc. (Behavioral Signals) was founded by the very people who created and pioneered many of the core technologies of emotion recognition and Behavioral Signal Processing, most notably the founder of BSP Dr. Shrikanth Narayanan and emotion recognition expert Dr. Alex Potamianos. The Signal Analysis and Interpretation Laboratory (SAIL) at the University of Southern California has explored under the leadership of Dr. Narayanan emotion recognition for over 15 years, leading to a first-of-its-kind umbrella patent on recognizing emotion from signals, for which Behavioral Signals has the exclusive license.
Behavioral and Emotional Analytics
Today, scientific advances in how we quantify unstructured signal data—like speech/audio and video—allow us to quickly gain understanding from large datasets. Such novel analytic methods form the expanding foundation, or backbone, of the Big Data movement. Speech and spoken language communication cues are an important means for measuring and modeling human behavior; with speech, it’s not just what a person says, it’s “how” they say it. Part of the “how” includes emotion: for example, was a customer angry, happy, or neutral? And will they buy/stay-on as a customer? But once we know the how, we all want to know the “why”! Why did they feel that way? Could the agent or business use a different strategy to improve the experience? This elusive KPI has traditionally been limited to human judgment such as from self-assessments by agents or customer complaints.
Whitepaper on Behavioral Signal Processing
Behavioral Signal Processing (BSP)1 is a recently proposed approach that employs state-of-the-art techniques to measure, analyze, and model human behavior directly from signals, with the ultimate goal of providing valuable information back to humans for making decisions. These computational techniques are now capable of understanding human expression and behavior, and have widespread applications in contact centers, marketing calls, health care, education, human-robot interaction, and beyond. BSP builds on popular methods like affective computing as well as core speech processing capabilities (e.g., intonation recognition and speech-to-text) and deep (machine) learning in order to understand the “how” and “why” of behavior, especially in human-human interaction.
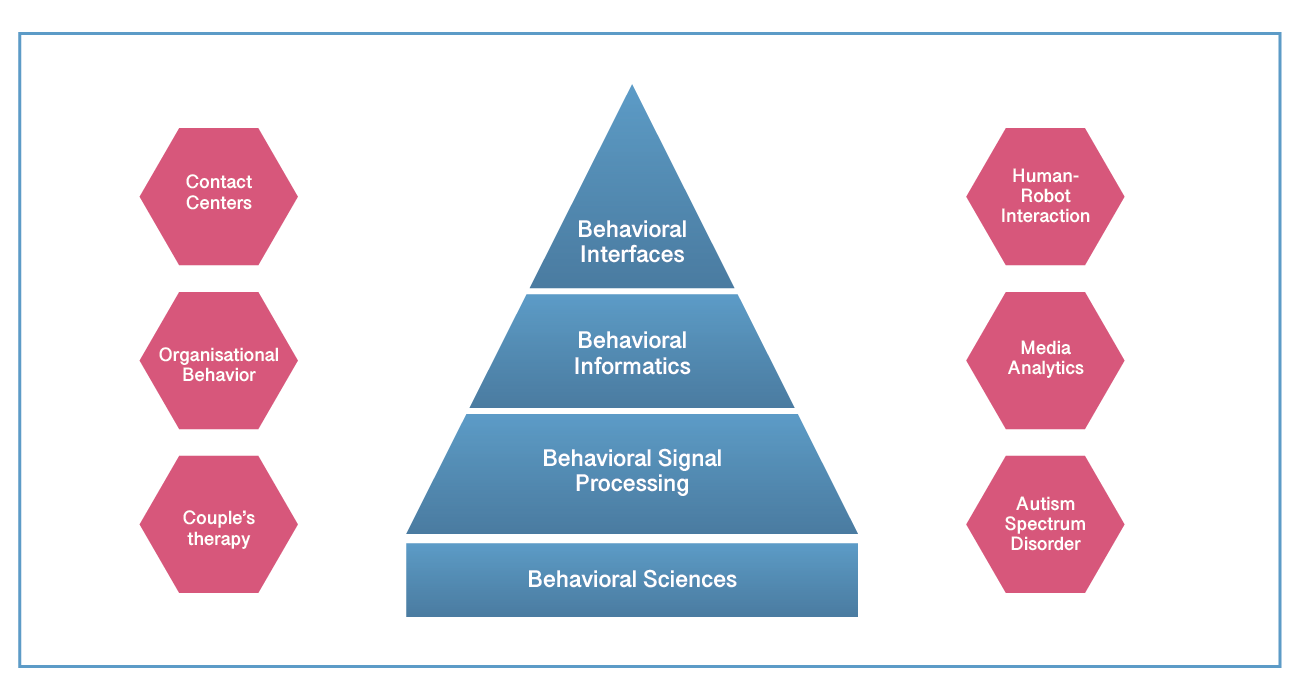
Fig.1b Behavioral Signal Processing (BSP) is the foundation for behavioral informatics and interfaces.
1 “Behavioral Signal Processing: Deriving human behavioral informatics from speech and language.” Shrikanth Narayanan & Panayiotis P. Georgiou. Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 101, no. 5, pp. 1203-1233, May 2013.
Discover more on Behavioral Signal Processing in
Read more
PAGES:
1 – Behavioral & Emotional Analytics | 2 – BSP in Healthcare | 3 – BSP for Media & Movie Analytics | 4 – BSP for Home Assistants & Robotics | 5 – BSP for Contact Centers | 6 – BSP for Organizational Behavior | 7 – Behavioral Signal Processing Pipeline: How it all works | 8 – Our Platform: callER & textER | 9 -The Challenges of Quantifying Behavior from Signals

